Almost everybody today knows what dopamine is. Or at least they think they do. It may seem strange for a neurotransmitter, but when you think about what dopamine is responsible for – motivation, cognitive performance, even mood and emotional stability – it makes sense that people would care a lot about this brain chemical.
Can nootropics raise dopamine? This is a common question asked online.
As people struggle to keep up with the demands of modern life, they often feel they need help staying motivated. That’s where nootropics come in.
There are a lot of nootropics on the market right now promising to help boost motivation. Many of the best nootropics promise to help keep you focused and motivated for hours on end, with many of them explicitly promising to raise dopamine levels.
So can nootropics really raise dopamine? To find out, let’s first take a closer look at what dopamine is, how it works in the brain, and then which nootropics might increase its production.
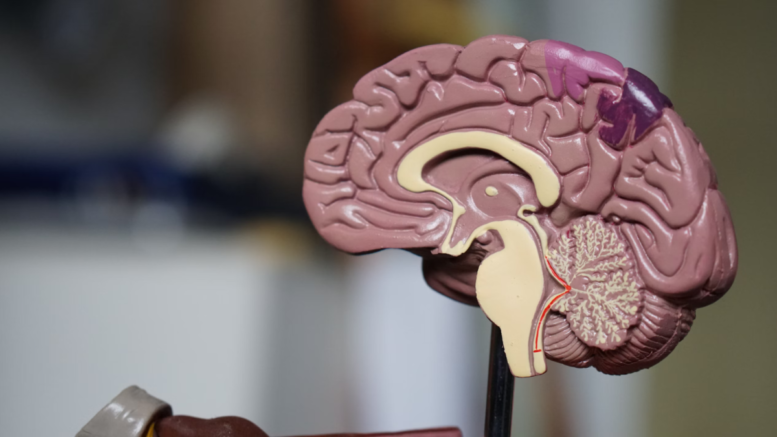
Dopamine: Learning about Rewards
Dopamine is only produced by a small number of neurons.
A decline of dopamine-manufacturing nerve cells in the substantia nigra is linked to cognitive decline – especially cognitive functions related to movement.
However, the roles of dopamine-releasing neurons in the ventral Tegmental Area (VTA), are not well understood. This makes their role and mechanism a contentious topic for neuroscientists.
Learning about rewards is one of the most important roles for VTA dopamine neuron.
VTA dopamine neurons are activated when there is a positive event. This could be a sudden supply of food, or a chance for leisure or procreation.
Although dopamine has a positive effect on human behavior, it also influences the addiction to most of the most commonly abused drugs. Dopamine causes the release of dopamine which is thought to be responsible for their addictive properties.
How Dopamine Works in the Brain
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter used by nerve cells to transmit messages. A neuron releases dopamine when it crosses a small gap known as a “synapse” and attaches with a dopamine receptor located on a nearby neuron.
Signals become blurred when dopamine levels in the brain are low. It’s like static on a TV or radio. Faulty signals can cause cognitive impairments such as moods, attention, learning, behavior and movement, and sleep.
Different brain areas produce different neurotransmitters. Dopamine production is mainly controlled by two brain areas:
Substantia Nigra
The substantia nigrais a small strip that runs across both hemispheres of the brain at the base, in a region known as the midbrain.
The substantia-nigra produces dopamine, which sends signals to movement. These signals can also influence speech. Movement can be impaired if dopamine-producing cells die in this area.
Extreme dopamine deficiencies can cause tremors, shaking, difficulty walking, eating, speaking, and inability to control movement. These symptoms can be alleviated by drugs, implants, and dopamine-stimulating dopamine supplements.
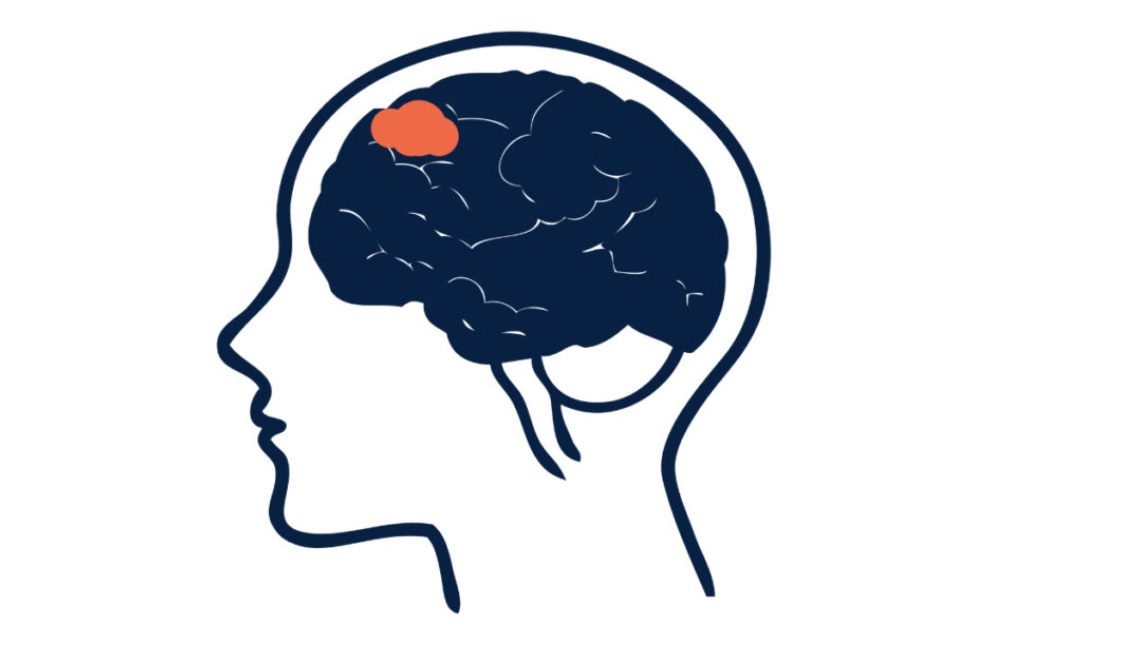
Ventral Tegmental area (VTA)
Another area in the midbrain that produces dopamine is the ventral-tegmental area (VTA). The VTA is an important part of motivation, thought, emotions and addiction.
However, learning is VTA dopamine’s most well-known function. The brain signals pleasure when VTA dopamine neurons are stimulated by good news. This mechanism is a reinforcement of behaviors that lead “rewards”, which leads to feelings of pleasure.
Mesolimbic Pathway
These two midbrain areas are smaller than a stamp but the dopamine they pump out carries messages throughout the brain, influencing cognitive function and mood in meaningful ways.
Dopamine sends messages through many pathways in the brain. The dopamine responsible for influencing mental constructs such as motivation, attention and addiction – the dopamine we’re really interested in here – mainly travels through the mesolimbic path.
This pathway is used by dopamine neurons in ventral tegmental to send messages to the nucleus accumbens and the cortex. It is here that dopamine really influences executive cognitive functions and behavior, and it is here that dopamine really influences motivation/reward-seeking behavior.
Can Nootropics Raise Dopamine?
The simple answer to this question is yes, nootropics can raise dopamine levels in the brain.
If you use the right nootropic substances, you can significantly increase dopamine levels in the brain, which in turn will leave you feeling more motivated, more ‘switched on’ and in a better mood.
Here are some of the most effective nootropics for raising dopamine levels.
Tyrosine
Tyrosine, an amino acid is, however, it is the best supplement to naturally increase dopamine levels. Tyrosine, a precursor of dopamine, is converted to LDOPA to make dopamine.
The brain can be stimulated to produce dopamine by taking Tyrosine. Clinical studies have shown that Tyrosine can significantly improve cognitive function in those who are subject to stressful or demanding situations (such as extreme cold or sleep deprivation). This is because Tyrosine increases dopamine, which helps you stay motivated, despite being tired or cold.

Nicotine
Nicotine is a powerful stimulant and a great nootropic to increase dopamine levels. Nicotine is a powerful dopaminergic nootropic. This is why nicotine is so addictive. It rapidly increases dopamine receptor activity and produces a feeling that relaxes, motivates, and mildly euphoric. Because dopamine builds reward-seeking behavior, it has people coming back again and again to nicotine, hence the addiction.
You don’t want nicotine addiction, but it can be a powerful and safe nootropic that can enhance many aspects of cognition, such as motivation and energy. We recommend using nicotine gum or patches to increase dopamine levels and motivation. Traditional tobacco products can have extremely harmful effects on your health.
Caffeine
Because caffeine is thought to increase energy, it isn’t on all the top nootropics for dopamine. When used properly caffeine can massively increase dopamine levels, enhance mental performance, and reduce fatigue.
This is a fact that caffeine can increase brain dopamine levels. But, unlike Tyrosine and caffeine, dopamine production is not increased by caffeine. Instead, caffeine alters dopamine receptors.
Research has shown that caffeine intake directly increases dopamine receptor accessibility in the brain. More specifically, it raises D2/D3 receptor availability within the ventral striatum. This could dramatically increase motivation as it would allow for greater activity at dopamine neuron. Researchers have found that caffeine users experience a significant increase in mental performance due to an upregulation of dopamine receptors.