A birth defect or congenital disability is an irregularity in how a baby’s bodily components develop or function. Although the condition is present from birth, it may not be identified later. Occasionally, the issue is passed down through generations. However, most of their origin remains unknown.
A health provider is critical in caring for a baby who has been born with a congenital disability. In addition, there are several methods that health providers use to look for birth defects.
Read on to know more about congenital disabilities and learn about the difference in the methods being used in diagnosing them.
How Are Birth Defects Diagnosed
Birth defects may be diagnosed based on the particular condition and the impaired areas or organs of the body. Moreover, numerous physical defects may be found and diagnosed during a newborn’s physical exam right after delivery. On the other hand, some disorders may only be detected and diagnosed by neonatal screening and prenatal diagnostics.
Here are some other methods health providers utilize to diagnose congenital disabilities.
Prenatal Screening
Women undergo frequent testing, such as blood work and urine tests to screen for diabetes, infections, or other pregnancy-related diseases throughout the pregnancy. These tests are called prenatal screening. Additionally, blood work identifies the amounts of specific compounds in a mother’s blood that indicate the baby’s likelihood of chromosomal diseases and genetic abnormalities.
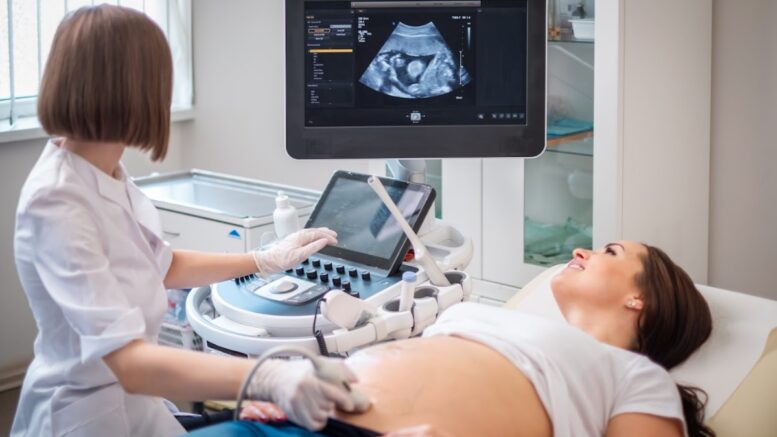
Moreover, ultrasound scans enable clinicians to examine the growing baby in the womb by producing an image through sound. Often than not, ultrasounds can diagnose some birth problems early on, like spina bifida.
In addition, specific pregnant women, notably those with a genetic history of some diseases, may benefit from further prenatal screening for birth abnormalities. Likewise, prenatal testing enables physicians to initiate therapy for some birth abnormalities as soon as possible.
Fetal Echocardiography
Fetal echocardiography is a procedure that employs sound waves to assess the heart of an unborn infant for cardiac abnormalities. This examination provides a more thorough view of the fetal heartbeat than a routine prenatal ultrasound does.
However, some cardiac problems are undetectable before birth, even with prenatal echocardiography. If your doctor discovers an abnormality in the formation of the child’s heart, a comprehensive ultrasound may be performed to rule out any other developmental concerns.

Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a procedure used to evaluate whether or not an unborn child has a genetic disease. In this procedure, a doctor uses a needle to extract a small quantity of amniotic fluid from the womb. After that, the cells are grown in a facility, and their genetic information is analyzed for any abnormalities.
However, due to the minor risk of miscarriage associated with amniocentesis, mothers should discuss the process with their physician before undergoing the test.
Amniocentesis is often given to mothers who have obtained an unusual result on a diagnostic test or who may be at increased risk. Moreover, the following are among the proteins that may be detected during amniocentesis.
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
AFP is a protein produced by the developing fetus. High levels of these proteins may indicate that the infant has a neural tube defect. It may also mean that the fetus has a body wall abnormality.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
AChE is an enzyme produced by the unborn infant. If a hole in the neural tube exists, this protein may travel from the fetus to the fluid around it, which may cause harm to the unborn child.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Like amniocentesis, this testing uses cells extracted from the mother’s womb to assess whether the baby has a genetic disease. The clinician extracts cells from the chorionic villi, which are found in the placenta.
On top of that, this test may be used to diagnose chromosomal abnormalities and other genetic diseases. Although CVS may be performed sooner in pregnancy, it’s linked with a marginally greater risk of complications than amniocentesis. Women contemplating undergoing CVS should speak with their doctor about the test and its associated risks.

Newborn Screening
Newborn screening is a procedure that examines the babies’ blood for a variety of health concerns, such as several birth abnormalities. However, it may not identify particular disorders but rather uncovers the possibility of a problem. By identifying issues shortly after birth, illnesses may be recognized and addressed before they have long-lasting consequences.
Additionally, newborn screening comprises hearing tests and pulse oximetry which is a test that measures the child’s heartbeat and oxygen levels. This may help discover important congenital heart issues.
Babies at an increased risk of developing certain diseases may undergo other tests at birth to identify and manage them if necessary. This kind of testing has been successful in identifying certain instances of Menkes disease, enabling therapy to start before the onset of health concerns.
Conclusion
A health provider may prescribe a range of exams, testing, and imaging procedures throughout pregnancy. These procedures are intended to give information on your baby’s growth and wellbeing. These may also assist you in optimizing your child’s prenatal care and development to diagnose birth defects early on.