Although male fertility gradually declines with age, the effect of aging on infertility is far greater in women. Along with aging, complications regarding hormonal dysfunction, ovulation disorders, and even unexplained reasons can cause the inability to conceive a baby.
According to a publication on the NICHD website, around 11% of women experience infertility in the United States. The primary symptoms include being unable to get pregnant even after one year of unprotected sex for women in their 20s or early 30s. The time frame will be 6 months if a female is aged over 35 years.
Infertility in women – symptoms & treatment can be changed depending on the underlying cause in the female body.
However, with the help of technological advances and extensive research, the medical sector of reproductive health now has multiple treatment options to cure female infertility.
In this article, we have discussed the possible symptoms you may find familiar if you are infertile. The treatment will be based on the diagnosis of which part of the reproductive system is malfunctioning, whether it’s related to hormones or to organic disorder.
What are the Symptoms of Women’s Infertility?
In addition to experiencing difficulty conceiving a child, symptoms might differ greatly from one individual to the next. The inability to conceive is the primary indicator of infertility which the following reasons may cause:
- Hypothalamic Dysfunction,
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS),
- Primary Ovarian Insufficiency,
- Cervical causes or
- Endometriosis uterine.
Due to these reasons, your ovulation and menstrual cycle change, and you may experience symptoms that indicate infertility. Endometriosis is a common reason for most period-related issues in which womb tissues are found in other places of the body.
Irregular Menstrual Cycle:
You may not be ovulating if your menstrual cycle is-
- Excessively lengthy, for example, it lasts for 35 days or more,
- Too brief, as it lasts less than 21 days,
- Irregular, or
- Nonexistent.
Indeed, additional symptoms may not even be present.
Abnormal Bleeding:
Lighter or heavier bleeding can point to infertility. With the help of a menstrual cup, you can measure how much blood you are losing.
Normally, 5ml to 80ml is the average amount of blood a female body can lose per period. This is about 6 tablespoons. If you are losing more or less blood than this amount, you should consider this abnormal.
Changing the Color of Period Blood:
There may be a problem if menstruation blood is consistently lighter in color than usual. When a woman first starts menstruating, her blood is a vivid red, but it can gradually turn darker as the period progresses.
Dark, old blood loss at the start of menstruation might also indicate endometriosis and later infertility.
Painful Period:
Pain in the lower abdomen is normal during menstruating since your ovary is enlarged with blood. However, with heating or painkiller, one can keep the pain at a bearable level.

If you are having unbearable cramping in addition to pelvic pain or back pain, medically, it is considered a symptom of infertility-related issues. You may experience chronic or acute pelvic pain during a period or at a different time.
You may also suffer from unpredictable vaginal bleeding or no period for a prolonged period of time. You may also feel fatigued, have bowel problems, or nausea.
Hormonal Issue-Related Symptoms:
At different stages of our lives, hormonal imbalance is quite normal. However, it may cause low libido, energy, or mood. You can take a private hormone blood test which can help your doctor figure out your hormonal profile and the possible imbalance so that they can help you treat the issue.
In the female body, fluctuations in hormonal balance can often be a symptom of infertility. In this case, you may face the following symptoms:
- Weight gain unexpectedly,
- Thinning hairline,
- Skin diseases (severe acne),
- Cold hands and feet,
- Abnormal hair growth in the chest, lips, or chin,
- Higher or lower libido (sexual desire or drive).
Other Symptoms:
Although the following symptoms appear due to infertility, they may also happen for other reasons.
Painful Sex:
Pain during sexual activity, also known as dyspareunia, can indicate a more serious underlying health issue that may affect a woman’s fertility. Infections, endometriosis, and fibroids are a few examples of the kinds of health problems that fall into this category.
Milky white discharge (unrelated to breastfeeding) from nipples:
It is essential to discuss with your physician any symptoms that seem unusual. Even if you are not actively trying to conceive, you should still seek medical attention for any of these symptoms because they could indicate underlying hormonal issues that may cause infertility later.
Is It Possible to Have Periods and Still Have Fertility Issues?
Having consistent and predictable cycles is a good indicator that ovulation occurs consistently. To put it another way, it indicates that your ovaries are producing an egg on a consistent basis, which is necessary for pregnancy. However, ovulation by itself does not ensure that a woman will be able to become pregnant.
Egg quality, the process by which an egg is fertilized, the egg’s capacity to be carried to the uterus, or the process by which it becomes implanted in the uterus can all provide challenges from time to time. There is also a possibility that there is an issue with the sperm.
What are The Treatment Options for Female Infertility?
The treatment options for female infertility can seem overwhelming to you because medical science in the reproductive sector has developed magnificently with the advancement of technology.
After diagnosing the underlying medical cause for infertility in your body, your physician may suggest you any of the possible treatments depending on the cause.
But do you have any knowledge on what are the costs of fertility treatments and how does it all work? Here is a short discussion for you to understand complicated medical terms in an easy way.
Depending on how severe the underlying medical condition is, the possibility of treating infertility in females is 50%. However, the main factors physicians consider before starting treatment are age, previous pregnancy history, and timeframe of the infertility symptoms.
Here are the possible treatment options.
1. Medication:
Physicians use fertility drugs and hormones (in dosage form) to treat ovulation disorders and maintain the hormone level to help a woman ovulate.
Letrozole
Letrozole is a medication that, when taken orally, reduces a woman’s natural estrogen levels, causing her ovaries to produce eggs.
Cabergoline or Bromocriptine
Oral medications like bromocriptine and cabergoline are used to reduce excessive levels of the hormone prolactin, which can prevent ovulation from occurring. It stimulates the increased production of egg-maturing hormones in the ovaries.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) and other gonadotropins
Ovulation can be induced by injecting a woman with a gonadotropin which includes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to stimulate the development of an egg follicle.
2. Surgery:
Surgery is necessary for women who are suffering from reproductive organ-related issues. For example, blocked fallopian tubes, or endometriosis. Even though the cause and symptoms are different from one woman to another, doctors diagnose blocked tubes by hysterosalpingogram test.
Tubal Cannulation:
Doctors perform surgery to clear the blockage of fallopian tubes.
Tubal Ligation Reversal:
In this surgical procedure, physicians work with blocked, knotted, or tied fallopian tubes to untie, reopen or reconnect them to make the ovulation process run again.
Other than surgery and medicine, physicians are taking the help of ART or Assisted Reproductive Technology. A few treatment options are:
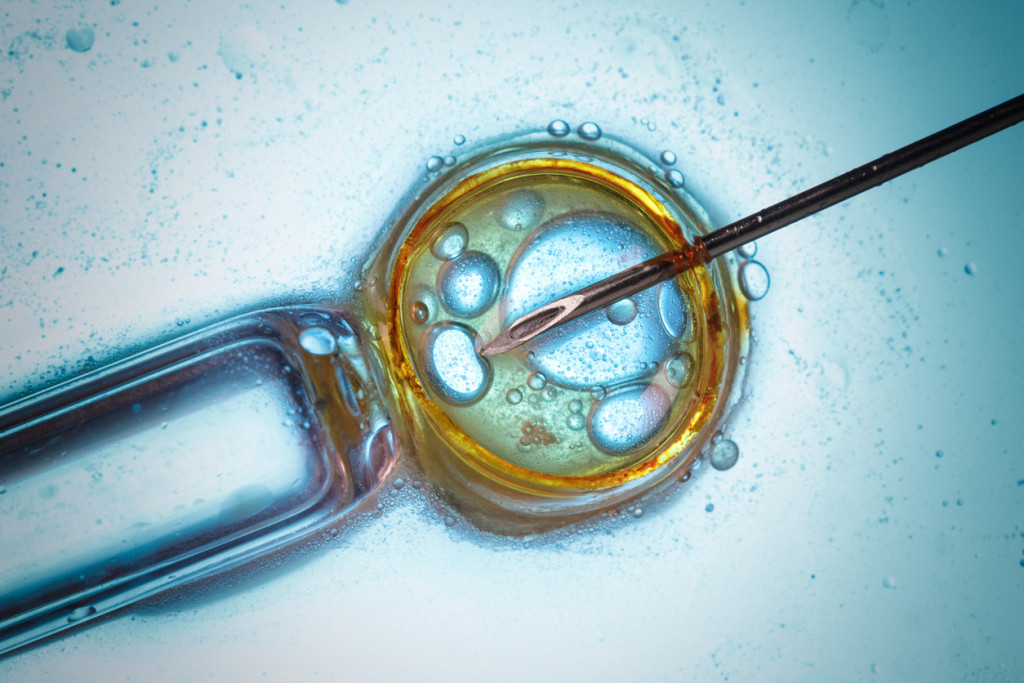
IVF or In-Vitro Fertilization:
Due to the difficulty of egg implantation in the uterus walls, many women cannot conceive a baby even though their partner and they are both fertile separately.
IVF or In-vitro fertilization, is a technique where the egg and sperm are fertilized in a controlled environment with the supervision of expert medical personnel. In-vitro means performing any biological option outside a living organism.
After successful fertilization, the egg stays and grows in the petri dish for another 3 to 5 days. The physician then places the embryo (fertilized egg, a few days after fertilization) in the uterus with a surgical procedure.
Artificial Insemination:
In this procedure, the doctor directly inserts sperms into the walls of the uterus or fallopian tube. This treatment has obtained a high success rate.
Using an Egg Donor:
Egg donation is the practice of obtaining an egg cell, or oocyte, from a donor for use in in vitro fertilization. The donor’s ovaries are stimulated to generate numerous eggs before the procedure begins.
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) or Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer):
After collecting the sperm and egg, they are immediately inserted into the fallopian tube. The GIFT procedure involves inserting both the eggs and the sperm into the fallopian tube.
In the ZIFT procedure, physicians proceed with in-vitro fertilization in the laboratory to produce a fertilized egg, which is then transferred to the tube after 24 hours.
Intrauterine Insemination:
During the time that the woman is ovulating, the sperm is collected from the male partner and deposited directly inside her uterus.
Although studies have shown that removing endometriosis patches through surgery increases the chances of pregnancy double-fold, the success rate for fallopian tube-related surgeries is relatively low (around 20%).
Also, it can lead to an ectopic pregnancy which is pregnancy in the fallopian tube or outside the uterus. Therefore, finding skillful and experienced surgeons is a must.
Quick Note:
A diagnosis of a condition that may reduce egg quantity and quality may prompt you to think about egg freezing even earlier.
When possible, we advise egg freezing for women in their late twenties or early thirties to increase their chances of becoming pregnant.
It safeguards your potential to start a family when you’re ready, even if it turns out to be far later in life.
As a bonus, you’ll have healthier eggs and fewer complications during pregnancy. Learn more about basic info about egg freezing.
Conclusion
The most significant element of this journey of conceiving a baby after failing numerous times in determining the cause of infertility in women.
Many medical tests are required, and you may have to undergo several trial-and-error procedures to make the miracle happen.
Now that you’ve learned about infertility in women – symptoms, and treatment, you should see a doctor if you find any similarities in the symptoms listed in this article.
