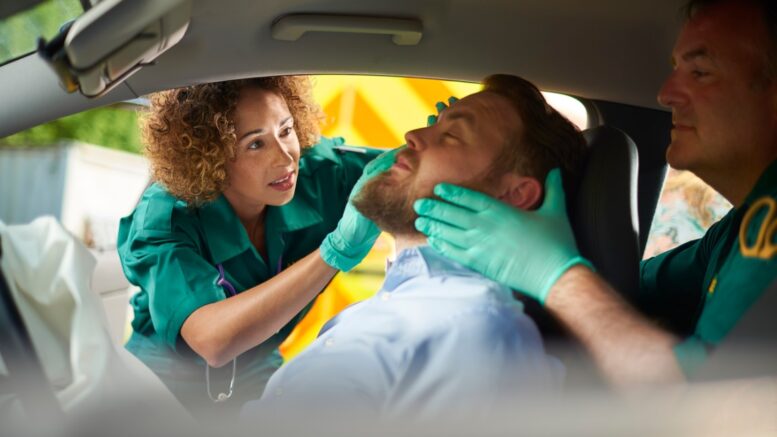
When there is a sudden increase in pressure inside the skull, it can cause fractures in the brain. Traumatic brain injury can also be caused by a violent blow to the head or body, or an object going through the brain tissue. If you experience any of these through negligence, such as a car accident, make sure to contact a traumatic brain injuries attorney.
Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
The cause of TBI depends on the nature of the head injury. The most common cause is a traffic accident.
Automobile, truck and motorcycle crashes
The National Safety Council estimates that in 2020, 42,060 people died in vehicle crashes. This is the first increase in four years and it’s 8% higher than last year. The fatality rate per 100 million miles driven spiked 24% last year, due to the increased use of autonomous vehicles.
This year, there will be approximately 4.5 million people who are seriously injured in car accidents. Of these many injuries, those affecting the brain are some of the most devastating.
Falls
This is the most common cause in adults aged 65 and older. Traumatic brain injury is a serious condition that can have a tremendous impact on someone’s life. There are many symptoms, but the one that can be especially damaging is that it makes people more susceptible to falls.
More than half of people with a traumatic brain injury are at an increased risk of falls. This means that the elderly are more likely to have exacerbated the effects of TBI with added symptoms.
Sports injuries
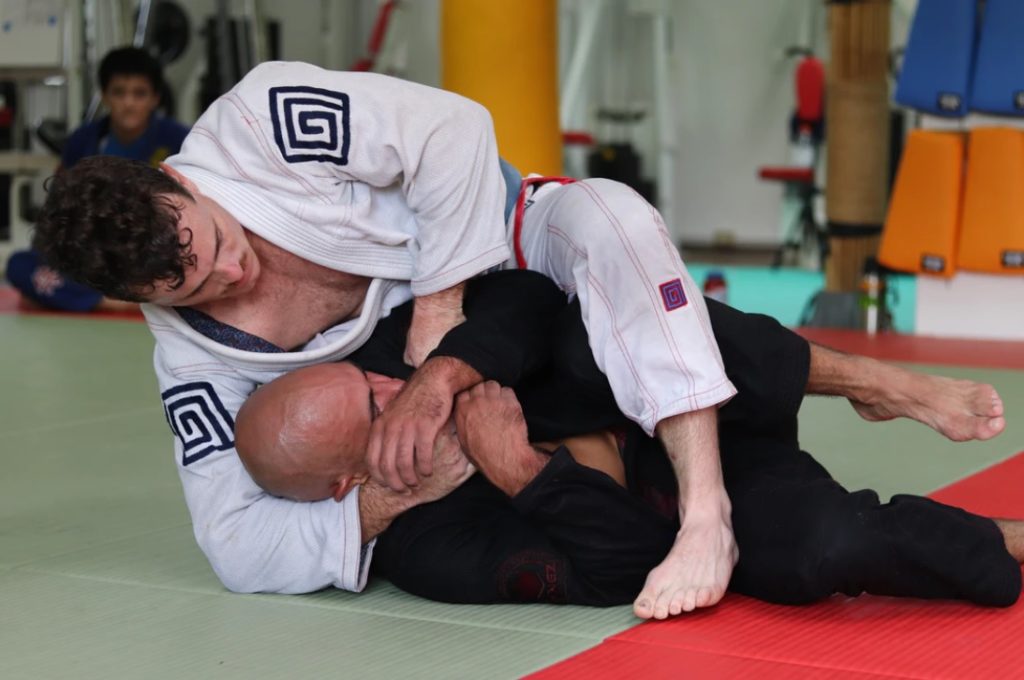

Of the estimated 1.7 to 3.8 million traumatic brain injuries that occur each year in the United States, 10 percent arise due to sports and recreational activities. Sports are a great way to keep fit and healthy, but they can also cause serious brain injuries. For every year that goes by, the number of head trauma injuries in kids is growing.
It’s not uncommon to sustain an injury while playing sports. In fact, these injuries can range from a mild physical trauma like a scalp contusion or laceration all the way to severe TBI with concurrent bleeding in the brain or coma.
Child abuse
This is the most common cause in children under age 4. Roughly one third of the children with cranial trauma per year in the United States are under 16 years, with more than half of these dying. Traumatic brain injury is a leading cause of death and disability in children.
According to the Journal of Medicine and Life (JML):
- The most common causes of TBI in children 0–13 years old were falls, in 173 cases (55.45%), falls from the same level 102 cases (32.70%), and falls from other level 71 cases (22.75%).
- Motor vehicle accidents have been the second leading cause of TBI for infants and toddlers in 74 cases (23.72%), pedestrians 56 cases (17.95%), and passengers 18 cases (5.77%).
- Other cases were accidental when struck of the head in 39 cases (12.50%), assaults/child abuse in 26 cases (8.33%).
Pediatric abusive head trauma (AHT), often called shaken baby syndrome, is a serious and sometimes life-threatening condition. AHT is caused by abusive head injury to an infant or young child.
Other terms relating to shaken baby syndrome include:
- Whiplash shaken infant syndrome (WSIS)
- Shaken impact syndrome (SIS)
- Inflicted traumatic brain injury (TBI)
- Nonaccidental head trauma (NAHT)
- Nonaccidental head injury (NAHI)
Blast injuries due to explosions
Military Service members are exposed to additional threats that normal people do not have to worry about. These include exposure to explosive blasts and its unique effects on the body.
Civilians most often are injured by blast injuries on the job or in certain sports. Head trauma can be caused by head-to-head contact, head-to-ground contact, or helmet impact. The leading cause of death from head trauma is the brain swelling.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Symptoms of Mild TBI
A brief loss of consciousness in some cases. However, many people with mild TBI remain conscious after the injury.
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Blurred vision or tired eyes
- Ringing in the ears
- Confusion
- Fatigue
- Mood or behavior changes
- Altered sleep patterns
- Problems with memory, attention, and concentration
Moderate or severe TBI. In addition to the above symptoms can include:
- Worsening headaches that become chronic
- Nausea or repetitive vomiting
- Seizures and/or convulsions
- Inability to wake up from sleep
- Heightened confusion, agitation, or restlessness
- Slurred speech
- Larger than usual pupil (dark center) of one or both eyes (dilation of the pupil).
- Numbness and/or weakness in the arms and legs
- Loss of coordination
Treatment for TBI
Mild TBI:
The first thing health care providers will do is stabilize you to prevent further injury. They will manage your blood pressure to make sure that the pressure inside of your skull stays normal, check the pressure in your head, and make sure enough blood and oxygen to your brain.
Moderate to Severe TBI
Medicines to remedy the symptoms of TBI and to reduce associated risks such as:
- Anti-anxiety medication to minimize feelings of fear and nervousness
- Anticonvulsants to avert seizures
- Antidepressants to treat depression and fluctuation of mood
- Stimulants to improve alertness
- Muscle relaxants to decrease muscle spasms
- Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
Surgery to reduce additional damage to your brain, for example by:
- Removing hematomas (clotted blood)
- Removing damaged or dead brain tissue
- Relieving pressure in the skull
- Repairing skull fractures
Rehabilitation therapies can improve the quality of life for those struggling with physical, emotional, and cognitive difficulties. These therapies include therapeutic exercise programs, mental health counseling, and other types of rehabilitative care.
Brain injury can be devastating. A TBI can lead to permanent disabilities and put one at risk for serious health problems such as depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
