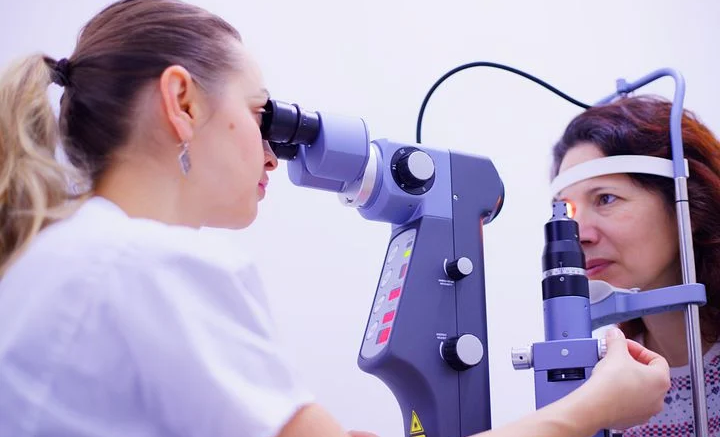
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that can result in vision loss if not treated. If you have diabetes, it’s essential to know what to look for so you can get treatment as soon as possible. Here’s what you need to know about diabetic retinopathy.
1 – What Exactly Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the tissue at the back of the eye that is sensitive to light. It’s a complication of diabetes, leading to vision loss and blindness. Diabetic retinopathy often affects both eyes. Left untreated, it progresses slowly from mild to severe. In mild diabetic retinopathy, there may be no noticeable symptoms.
As the disease progresses, you may experience blurred vision and difficulty seeing at night. Advanced diabetic retinopathy can result in vision loss and blindness. If you have advanced diabetic retinopathy, you may need surgery to repair or replace damaged blood vessels in your retina. Surgery is also an option if blood vessel blockages are causing decreased vision.
With proper treatment, many people with diabetic retinopathy can keep their vision. However, for diabetics, the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy is higher than if you don’t have diabetes. Other factors that may increase your risk include poor blood sugar control, high blood pressure, the length of time you’ve had diabetes, being pregnant, and having a family history of diabetic retinopathy.
2 – Who Is Most At Risk For Diabetic Retinopathy?
The longer you have diabetes, the greater your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. That’s why it’s essential to control your blood sugar levels and get regular comprehensive dilated eye exams. People with type 1 diabetes are usually diagnosed before age 18, so they’re more likely to develop diabetic retinopathy sooner than those with type 2 diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes are typically diagnosed after age 40. African Americans, Hispanic/Latinos, Native Americans, and Asian Americans also have a higher risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
If you have diabetic retinopathy, you may not have any symptoms in the early stages of the disease. That’s why getting regular comprehensive dilated eye exams is so important. These exams can detect diabetic retinopathy before it causes vision loss and other serious problems, such as detached retinas or glaucoma.
3 – How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Typically Diagnosed?
Diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam that includes dilation of the pupils. During the exam, a doctor will check for changes in the retina characteristic of diabetic retinopathy. These changes include leakage of blood vessels in the retina, thickening and swelling in the retina or growth of new blood vessels on the retina’s surface. In addition, pictures of the retina are taken during the exam to track the disease’s progression and plan treatment.
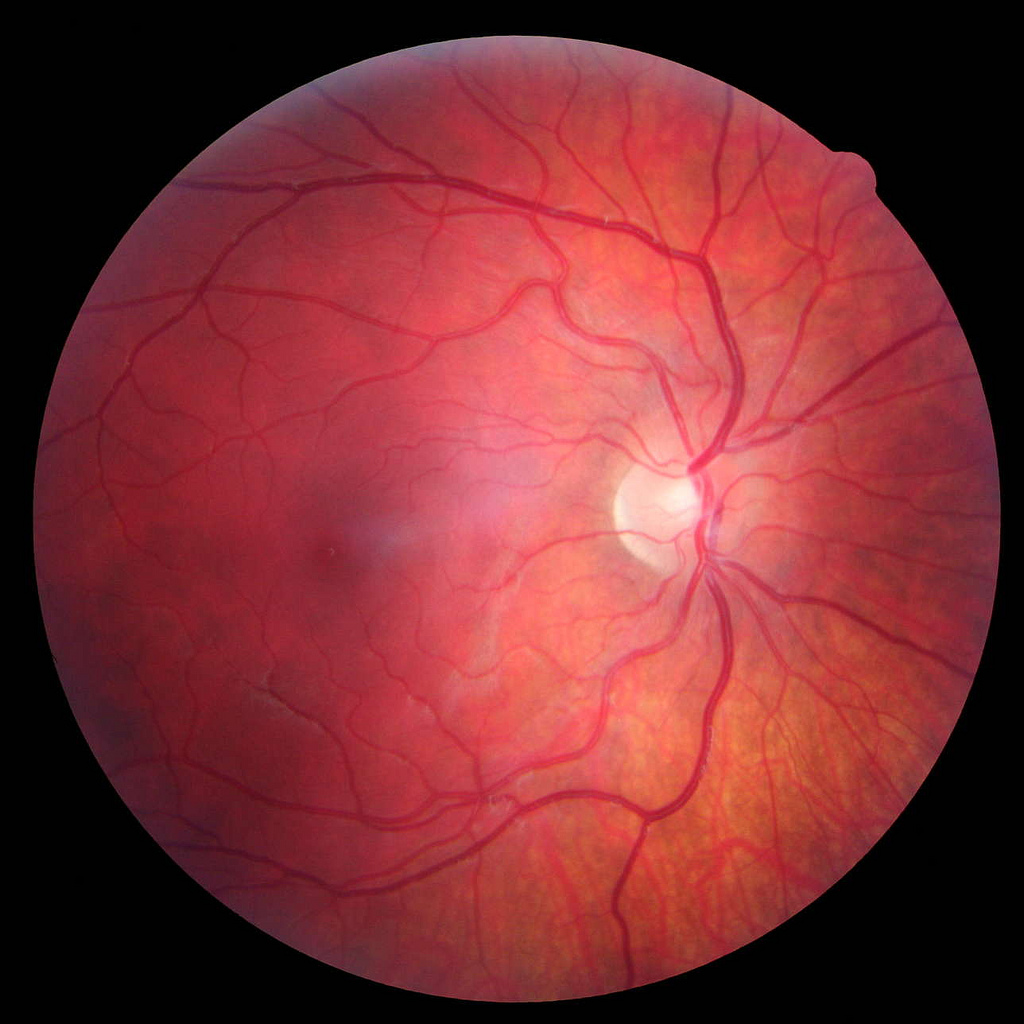
Two types of eye exams can be used to diagnose diabetic retinopathy: a comprehensive dilated eye exam and a screening test called fundus photography.
A comprehensive dilated eye exam is the best way to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy because it allows your doctor to fully evaluate your eyes’ health. In this exam, your doctor will place drops in your eyes to dilate your pupils. This allows him or her to better view the retina — the rear part of your eye — and look for signs of diabetic retinopathy.
Fundus photography is a screening test that uses special cameras to take pictures of the back of your eye. These detailed pictures can track any changes in your retina over time. If you have diabetes, you should have this test at least once a year.
If you develop diabetic retinopathy, you will likely need to have follow-up examinations more often so that your doctor can monitor the progression of the disease and plan treatment accordingly.
4 – What Is The Treatment For Diabetic Retinopathy?
The first step in treating diabetic retinopathy is to see your doctor for a comprehensive dilated eye exam. During this exam, your doctor will look for signs of diabetic retinopathy and other eye problems. If caught early, diabetic retinopathy can be treated with laser surgery. This surgery involves making tiny burns around the area of leaking blood vessels to seal them off. In some cases, laser surgery may also be used to shrink abnormal new blood vessels.
If your diabetic retinopathy is more advanced, you may need a different type of treatment called vitrectomy. This surgery involves removing the blood from the eye’s middle so that new blood vessels are less likely to grow and leak. Vitrectomy can also help repair any retina that has been detached due to diabetic retinopathy. After vitrectomy surgery, you may need to have cataract surgery as well.
5 – Is There Any Way To Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy often has no early warning signs, so it’s crucial to get a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year if you have diabetes. Here are three ways you can prevent diabetic retinopathy:
1. Keep your blood sugar levels under control
The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to keep your blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible. If you have diabetes, you must control your blood sugar levels tightly. You can do this by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking your medication as prescribed. If you’re having trouble controlling your blood sugar levels, talk to your doctor about adjusting your medication or insulin regimen.
2. Take care of your overall health
In addition to Tightly controlling your blood sugar levels, you also need to take care of your overall health to prevent diabetic retinopathy. That means eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and managing stress. These factors can help improve your blood sugar control and reduce your risk for diabetic retinopathy.
3. Get regular eye exams
As we mentioned before, diabetic retinopathy often has no early warning signs. That’s why it’s so important to get a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year if you have diabetes. During a dilated eye exam, an eye care professional will examine your retina for signs of damage and make sure that diabetic retinopathy is detected early so that it can be treated effectively.
Wrap-Up: Diabetic Retinopathy Is Serious But Preventable
Diabetic retinopathy is a preventable condition, and it’s essential to get checked regularly by an ophthalmologist. If you think you may be at risk for diabetic retinopathy, please make an appointment with an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to keep your vision healthy for years to come.
