High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, is a common condition that affects millions of people in the U.S.A. The condition of diabetes, which is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, affected about 34.2 million adults in the United States as of 2020, or almost 13% of the population. This statistic underscores the significance of addressing and managing high blood sugar to prevent complications such as kidney damage.
While it is usually associated with diabetes, high blood sugar can have severe consequences for various organs in the body. One such organ is the kidneys, which are vital in filtering waste products from the blood. Research has shown a strong connection between blood sugar imbalance and kidney health, highlighting the importance of managing blood sugar levels effectively.
In addition to the awareness, medications like Metformin are an important tool in managing the blood sugar levels. The best part is that you can buy Metformin from Canada at affordable prices.
In this article, we will take a look at the link between high blood sugar and kidney health, while exploring the management strategies for kidney damage and high blood sugar levels.
The Importance of Kidneys & High Blood Sugar Effects
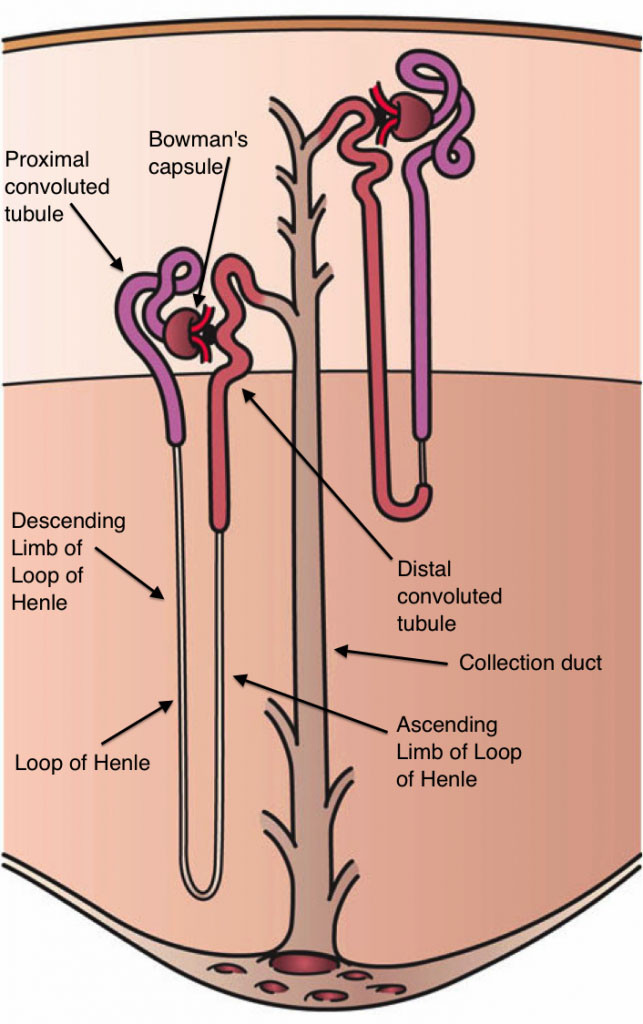
The kidneys are in charge of clearing out waste and excess fluids from the bloodstream, maintaining a delicate balance of electrolytes, and producing urine. However, when blood sugar levels are consistently high, it might harm the tiny blood vessels and filtering units within the kidneys, known as nephrons. Over time, this damage can lead to a condition called diabetic nephropathy, which is a common cause of kidney failure.
Because of high blood sugar, kidneys have to work harder to filter the blood, putting excessive strain on these vital organs. Additionally, elevated blood sugar levels can disrupt the intricate signaling mechanisms within the kidneys, impairing their ability to function optimally. As a result, waste products and fluids can accumulate in the body, leading to a range of complications.
Furthermore, chronic high blood sugar levels can promote inflammation and oxidative stress, which further contribute to kidney damage. The inflammation can lead to scarring and fibrosis within the kidneys, reducing their efficiency in filtering waste products. On the other hand, oxidative stress results in cellular damage within the kidneys when there is an imbalance between the body’s ability to neutralise harmful free radicals and the creation of those molecules.
How Does High Blood Sugar Affect Kidney Health in the Long Run?
In the long run, excessive blood sugar levels can have a significant impact on kidney health, leading to a condition known as diabetic nephropathy or diabetic kidney disease. Let’s explore how high blood sugar affects the kidneys over time and the potential consequences if left untreated or uncontrolled.
- Gradual Kidney Damage: Persistent high blood sugar levels can damage the small blood vessels and filtering units in the kidneys, known as nephrons. This damage can occur over a period of years, initially causing small amounts of protein leakage into the urine, a condition called microalbuminuria. If blood sugar levels remain elevated, the kidney damage can progress to significant protein loss in the urine, known as macroalbuminuria.
- Declining Kidney Function: As diabetic nephropathy progresses, the kidneys’ ability to filter waste products and excess fluid from the blood diminishes. This decline in kidney function can lead to a formation of toxins and waste products in the body, contributing to complications such as high blood pressure and fluid retention.
- Development of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): If left untreated or uncontrolled, diabetic nephropathy can eventually cause the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD is characterized by a gradual and irreversible loss of kidney function over time. The kidneys become less efficient in filtering waste products, regulating electrolyte balance, and maintaining fluid balance in the body.
- End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): In some cases, diabetic nephropathy can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), also known as kidney failure. At this stage, the kidneys are no longer able to function adequately to sustain life. Treatment options for ESRD include dialysis, a process that involves using a machine to filter waste products and extra fluid from the blood, or a kidney transplant.
To mitigate the risk of diabetic nephropathy and kidney damage, it is crucial for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. This includes adhering to a well-balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, taking prescribed medications as directed, and closely monitoring blood sugar levels. Regular medical check-ups, including urine tests to assess protein levels, are important for early detection and intervention.
Early detection and intervention are vital in slowing down the progression of kidney damage and preserving kidney function. Blood pressure control, management of other cardiovascular risk factors, and working closely with healthcare professionals are also important components of kidney health management in individuals with diabetes.
By effectively managing blood sugar imbalance and taking proactive measures to protect kidney health, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy and its complications, promoting overall well-being and longevity.
Managing High Blood Sugar and Kidney Damage
To stop or delay kidney damage’s progression, controlling blood sugar levels is paramount.
Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables, along with regular exercise, helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports kidney health. Engaging in aerobic exercises and strength training improves insulin sensitivity and overall cardiovascular health.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital for effective management. Managing other risk factors, including high blood pressure and cholesterol levels also contributes to kidney health. By embracing a healthy lifestyle and addressing blood sugar control, individuals can proactively protect their kidneys and reduce the risk of kidney damage.
Additionally, medications like Metformin are usually prescribed to individuals with type 2 diabetes. Metformin, a blood sugar formula, lowers blood sugar levels by limiting glucose production in the liver and enhancing insulin sensitivity. U.S.A. citizens can look for the best Canadian online pharmacy for convenience and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
Managing high blood sugar is crucial for preserving kidney health and reducing the risk of complications. By understanding the relationship between blood sugar imbalance and kidney function, individuals can take proactive measures to control their condition and promote overall well-being.
Working closely with healthcare professionals, adhering to a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and monitoring blood sugar levels are key strategies for managing high blood sugar and protecting kidney health.
Taking control of your health today and implementing these lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to maintaining optimal blood sugar levels and supporting kidney health in the long run. By prioritizing your well-being and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, you can take proactive steps towards managing high blood sugar and promoting overall kidney health.