Regenerative treatments have emerged as a groundbreaking approach to address joint and bone issues. These therapies harness the body’s innate healing abilities, holding the potential to alleviate symptoms, revive mobility, and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from musculoskeletal conditions.
This article explores the science behind regenerative medicine, its impact on joint and bone ailments, potential benefits, as well as the limitations and risks associated with these treatments.
Understanding Regenerative Treatments
Regenerative treatments are medical procedures that use the body’s natural healing abilities to repair damaged tissues and organs. This approach includes therapies such as stem cell treatments, platelet-rich plasma injections, and tissue engineering.
The goal of these treatments is to help the body regenerate its own cells, thus restoring normal function and mitigating symptoms brought about by joint and bone issues. This process is aimed at not just treating symptoms, but addressing the root cause of the problem.
The Science Behind Regeneration
The science behind regeneration centers on the body’s remarkable ability to repair and renew itself. This is largely credited to the presence of stem cells, which are unique in that they can morph into different cell types.
In regenerative treatments, these cells are leveraged to repair damaged or degenerated tissues, such as those in our joints and bones. By stimulating cell growth and accelerating tissue repair, these treatments aim to restore function and alleviate symptoms associated with various musculoskeletal conditions.
Impact of Regenerative Therapies on Joint
Regenerative therapies have shown significant potential in treating joint issues. They work by initiating a healing response in damaged or degenerated joint tissues, such as cartilage, ligament, or tendon.
Through the injection of restorative cells or growth factors, these therapies can stimulate repair, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function. Consequently, they can help relieve pain, improve mobility, and enhance the quality of life for individuals suffering from joint diseases or injuries.
Reviving Mobility: Focus on Bone Issues
Regenerative treatments are also making strides in addressing bone issues. These therapies aim to stimulate the body’s natural bone-healing process, which can be slow or insufficient due to age, disease, or severe injuries.
By promoting the growth of new bone tissue and enhancing blood supply to the affected area, regenerative treatments can support bone repair and regeneration. The result is improved stability, strength, and, ultimately, mobility for individuals suffering from bone-related ailments.
Potential Benefits of Regenerative Treatments
Regenerative treatments possess vast potential for addressing various health concerns. The benefits of these therapies extend beyond mere symptom management.
Cellaxys treatments, for instance, target the root cause of the issue, facilitating healing and recovery through the body’s innate regenerative capabilities.
Let’s delve deeper into several significant regenerative treatments that are currently making waves in the medical field.
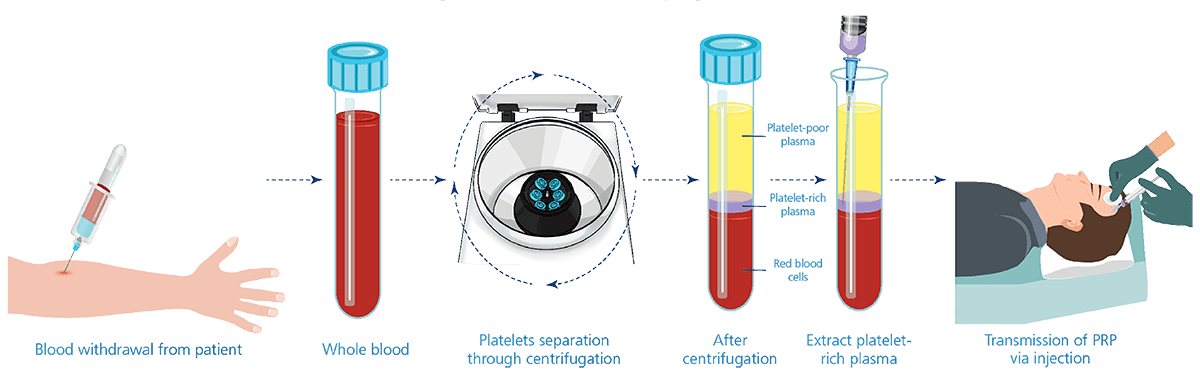
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
PRP is a renowned regenerative treatment widely used by top athletes in the early 2000s. It involves drawing a person’s blood, concentrating the platelets in plasma through centrifugation, and injecting this platelet-rich plasma into damaged tissue.
The platelets, packed with growth factors and anti-inflammatory proteins, can enhance healing and alleviate symptoms. PRP has been successfully used to address osteoarthritis pain, damaged tendons, and even hair loss and aging skin.
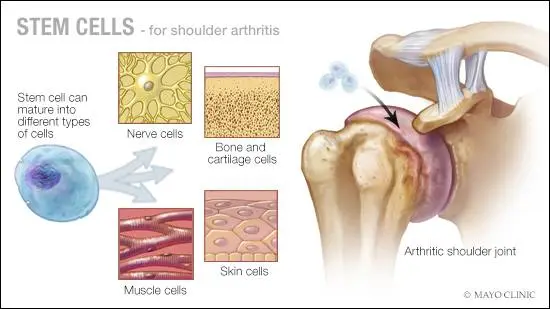
Stem cell therapy
Arguably the most well-known regenerative treatment, stem cell therapy utilizes the versatile nature of stem cells, which can morph into any cell type. This makes them ideal for regenerating deteriorated cartilage and ligaments in joints.
The process involves extracting stem cells—usually from the patient’s bone marrow—and injecting them into the problematic joint to stimulate healing. This approach has proven particularly useful in managing joint and tissue damage.
Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy, another type of regenerative medicine, harnesses the body’s natural healing response without requiring blood draws or stem cell harvesting. In this procedure, a safe glucose solution is injected into the affected joint to stimulate the body’s defense and healing mechanisms.
Autologous microfragmented adipose tissue (AMAT or MFAT)
AMAT, also known as fat-based PRP, involves removing a small amount of fat from the patient, processing it, and injecting it into the treatment area.
The fat, rich in stem cells and other regenerative cells, can significantly improve symptoms of various conditions, including osteoarthritis, back pain, and tendon and meniscus tears.
Regardless of a patient’s age, weight, or arthritis stage, microfragmented fat has shown the potential to improve pain and function.
Possible Drawbacks and Risks
Like all medical interventions, regenerative treatments come with their own set of limitations and potential complications. Let’s examine the potential challenges linked with the aforementioned treatment types.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
- The composition and effectiveness of PRP can vary based on several factors, including the preparation method, centrifuge type, time of day, and even the patient’s diet. This variability may lead to inconsistent study results.
- PRP therapies may only provide symptom relief, not tissue regeneration. While they can alleviate discomfort, evidence suggests that they may not restore damaged structures.
Stem cell therapy
- It’s challenging to cultivate adult stem cells for extended periods in culture. We currently lack the technology to produce these cells in large quantities, limiting their potential and application.
- There may be issues with maintaining and reproducing stimulated pluripotent cells, further complicating results.
Prolotherapy
- Although no reports are available, it’s possible to experience side effects like allergic reactions, infections at the injection site, nerve damage, and lightheadedness.
Autologous microfragmented adipose tissue (AMAT or MFAT)
- The quality of AMAT depends on how fat is collected and the device used for purification. This variability can affect the treatment’s overall effectiveness.
- More research and data are needed to validate AMAT’s potential and determine its optimal application and efficacy.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine in Treating Joint and Bone Issues
The future of regenerative medicine in managing joint and bone issues is promising. While there are challenges and limitations, continuous research and advancements in the field are paving the way for more effective and targeted treatments.
Adaptability, refinement, and understanding of these therapies continue to evolve, opening new avenues for improving patient outcomes and quality of life. The goal is not just relief from pain or discomfort, but true healing and revitalization—a vision that regenerative medicine is striving to make a reality.